
StudySmarter: Study help & AI tools
4.5 • +22k Ratings
More than 22 Million Downloads
Free
Struggling to grasp the intricate equations, laws, and theories in your Engineering studies? Look no further! StudySmarter is designed to make your learning experience easier and more productive. We simplify complex engineering concepts into easy-to-understand language to help you make the most of your study time.

Lerne mit deinen Freunden und bleibe auf dem richtigen Kurs mit deinen persönlichen Lernstatistiken
Jetzt kostenlos anmeldenStruggling to grasp the intricate equations, laws, and theories in your Engineering studies? Look no further! StudySmarter is designed to make your learning experience easier and more productive. We simplify complex engineering concepts into easy-to-understand language to help you make the most of your study time.
Imagine a completely free app that deconstructs complicated engineering theories into manageable knowledge chunks. Our goal is to streamline your learning process, providing comprehensive resources that cover everything from Engineering Mathematics to Engineering Thermodynamics. Our dynamic flashcards, which are customizable and interactive, help you memorise and deeply understand and apply what you learn.
Engineering is the application of scientific principles to design, build, and maintain structures, machines, devices, systems, and processes. It combines mathematics, physics, and often chemistry with a range of specialized knowledge specific to each engineering discipline. The overarching goal is to solve real-world problems, whether it's constructing a skyscraper that can withstand earthquakes, developing a new manufacturing process, or creating a medical device that improves human health.
Your Law revision time can be easy and free! Your answer is StudySmarter, an award-winning study app offering an extensive collection of summaries, flashcards, notes, quizzes, and more, covering all Law topics.
The StudySmarter app can be used online and offline at no cost to you. That’s correct; StudySmarter is a free study app.
Here’s why you should start your comprehensive Engineering exam prep with StudySmarter:
✔ Easy access to thousands of flashcards in Engineering topics - or you create your own directly from your study material!
✔ Free expert-verified summaries to guide you through crucial topics like Professional Engineering and Design Engineering.
✔ An intelligent study plan, complete with analytics and a study timer, to motivate you to pass your engineering modules and all other exams.
✔ Create study groups to share documents, notes, and flashcards. Perfect for a team project or a group study session!
And so much more! With StudySmarter, learning is accessible and fun!
The following modules are free the moment you sign onto our free app:
| Module Number | Area of Study | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Engineering Mathematics | Tackles calculus, statistics, and linear algebra relevant to engineering. |
| 2 | Solid Mechanics | Explains material properties, stress-strain analysis, and structural integrity. |
| 3 | Professional Engineering | Covers ethics, project management, and quality assurance in engineering. |
| 4 | Design Engineering | Focuses on product design, CAD, and the lifecycle of engineering projects. |
| 5 | Engineering Fluid Mechanics | Delves into fluid behaviour, flow patterns, and relevant calculations. |
| 6 | Engineering Thermodynamics | Covers heat transfer, energy systems, and thermodynamic laws. |
| 7 | Engineering Materials | Discusses types of materials, their properties, and applications. |
Engineering Mathematics is the cornerstone for all types of engineering disciplines. This module equips you with the tools to solve real-world problems using calculus, statistics, and linear algebra. For instance, imagine you are tasked with modelling the load distribution along a beam in a bridge; the calculus and linear algebra skills you acquire in this module will be instrumental.
Solid Mechanics provides you with the essential knowledge to understand the behaviour of solids under various types of stress and strain conditions. The module covers material properties, stress-strain relationships, and factors affecting structural integrity. A typical application could be in analyzing the forces acting on the fuselage of an aircraft and determining the best material for optimum performance and safety.
This module is crucial for understanding the broader context in which engineering operates. It covers aspects like ethics, project management, and quality assurance. Suppose you're leading a team to design a new eco-friendly vehicle. Professional Engineering will guide you in balancing design innovation with ethical considerations like sustainability and safety standards.
Design Engineering focuses on the planning and creation of new products and systems. You'll be introduced to Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software, and you'll learn the full life cycle of engineering projects from conception to completion. For example, if you were designing a new type of renewable energy wind turbine, this module would guide you through each step, ensuring functionality, efficiency, and ease of production.
Understanding the behaviour of fluids is crucial in sectors ranging from automotive design to energy production. This module delves deep into fluid behaviour, fluid dynamics, and the mathematical models used to predict flow patterns. An example application could be in the design of an efficient irrigation system that maximizes water delivery while minimizing waste.
In Engineering Thermodynamics, you'll study the principles governing energy transfer and transformation. This includes understanding heat engines, refrigeration cycles, and the laws of thermodynamics. For example, if you were working on improving the efficiency of an internal combustion engine, a solid grasp of thermodynamics principles would be crucial in making informed decisions.
Last but not least, the Engineering Materials module provides you with comprehensive knowledge about different types of materials like metals, polymers, ceramics, and composites, along with their properties and applications. For instance, if you're designing a lightweight but sturdy frame for a high-speed train, your choice of material would play a vital role, and this module would guide you in making the best selection.
Not sure about what your career opportunities are while studying Engineering with StudySmarter? Below is a brief summary of two fields of engineering you can pursue using our effective summaries and study plans.
Civil and mechanical engineering are both prominent branches of the engineering field, each with its own set of specializations, work environments, and job roles. While they may share some foundational engineering principles, the two disciplines are distinct in focus, application, and career paths. Here's a closer look at the key differences between civil and mechanical engineering.
Civil Engineering: Primarily concerned with the planning, design, construction, and maintenance of infrastructure projects like roads, bridges, buildings, water supply systems, and sewage treatment plants. It's about creating and enhancing the built environment.
Mechanical Engineering: Focuses on the design, analysis, and manufacturing of mechanical systems, which are essentially any system that has moving parts. This could range from engines and HVAC systems to robotics and biomedical devices.
Civil Engineering: Structural engineering, environmental engineering, geotechnical engineering, transportation engineering, water resource engineering, etc.
Mechanical Engineering: Automotive engineering, aerospace engineering, thermal engineering, biomechanical engineering, robotics, etc.
Civil Engineering: Often involves concepts from geology, environmental science, and geography, as well as strong emphasis on physics and mathematics.
Mechanical Engineering: Requires a strong understanding of physics, particularly mechanics, thermodynamics, and kinematics. Also includes principles from materials science and electrical engineering.
Civil Engineering: Infrastructure projects like dams, highways, sewage systems, bridges, and skyscrapers.
Mechanical Engineering: Products like vehicles, appliances, jet engines, and manufacturing equipment.
Civil Engineering: Work is often onsite, where engineers supervise construction and maintenance activities. Alternatively, they may be based in offices for tasks like planning and design.
Mechanical Engineering: Work environment varies widely, from office settings for design and analysis tasks to manufacturing plants or research labs for prototyping and testing.
Civil Engineering: Civil engineers often work for government agencies, engineering consulting firms, or construction companies. They may also specialize further, becoming structural engineers, transportation planners, or even city engineers.
Mechanical Engineering: Mechanical engineers are employed across multiple industries, including automotive, aerospace, energy, and healthcare. Career paths could lead to roles in research and development, manufacturing, or even software development for mechanical systems.
While distinct, the two fields can sometimes overlap. For instance, both disciplines might collaborate on a complex structure like a stadium, where mechanical systems for lighting, heating, and ventilation (mechanical engineering) integrate with the broader structure like beams, arches, and material selection (civil engineering).
StudySmarter offers more than just study aids; it equips you with a versatile skill set applicable in numerous sectors. Your ability to solve problems, communicate effectively, and interpret complex data will be honed to perfection. Take control of your engineering studies and pave the way for a successful career with StudySmarter. By using our completely free resources, you will be well prepared and confident for every level of exam.
Civil Engineering is a branch of engineering that focuses on the design, construction, and maintenance of the built environment, including structures like roads, bridges, dams, buildings, and water supply systems. It is a broad field that often incorporates elements of other engineering disciplines, such as mechanical and electrical engineering, to create more complex systems like transportation networks or waste management systems.
Mechanical Engineering is an engineering discipline that deals with the design, analysis, and manufacture of mechanical systems. This can range from designing a new engine for a car to creating a robotic arm for a manufacturing line. Mechanical engineers apply principles of physics, mathematics, and material science to solve engineering problems. They work in diverse industries such as aerospace, automotive, and energy sectors.
An engineer is a professional trained in the application of scientific and mathematical principles to develop solutions to technical problems. Engineers work in a wide range of industries, from civil and mechanical engineering to specialized fields like aerospace, electrical, and biomedical engineering. They are problem solvers at heart, using their knowledge and expertise to create, improve, and maintain various systems, structures, and products.
Educational Foundation
Bachelor's Degree
Internships/Co-op Programs
Licensing and Certification
Continued Learning
Engineering Design is the process of devising a system, component, or process to meet desired needs and specifications within constraints such as cost, time, and available resources. The process often begins with identifying a problem or need, followed by research and conceptualization to develop a range of solutions. These solutions are then evaluated, with one being selected for development and testing. Engineering design incorporates various elements like functionality, aesthetics, and usability to produce a final product or system that solves a specific problem effectively.
What is the main focus of Materials Engineering?
Materials Engineering is the study of the properties of materials, their processing techniques, and their applications in various sectors. It deals with the design, discovery and optimisation of new and existing materials.
Which elements play a key role in Materials Engineering?
The key elements in Materials Engineering are structure, properties, and processing. Structure refers to the atomic arrangement, properties to the characteristics of the material, and processing to the transformation of raw material into a usable form.
What role does Materials Engineering play in our daily lives and technology advancement?
Materials engineers contribute to every stage of product development. They ensure materials used are fit for purpose, economical, and sustainable. Their work, like developing sustainable plastics or medical implants, is central to technological progress and tackling global challenges.
What are the key properties of metals used in engineering?
Metals used in engineering are generally malleable, ductile, and good conductors of heat and electricity. They are known for their strength, which can be measured in terms of ultimate strength or yield strength.
How does the property of ductility influence the performance of engineering materials?
Ductility describes how much a material can be stretched or bent without breaking. This property is highly desirable in materials used in parts that require shaping or forming.
What are composites in the context of engineering materials and how do they work?
Composites are engineered materials designed to combine the best properties of their constituent materials. An example is fibreglass, which combines the strength of glass with the flexibility of polymer resin.
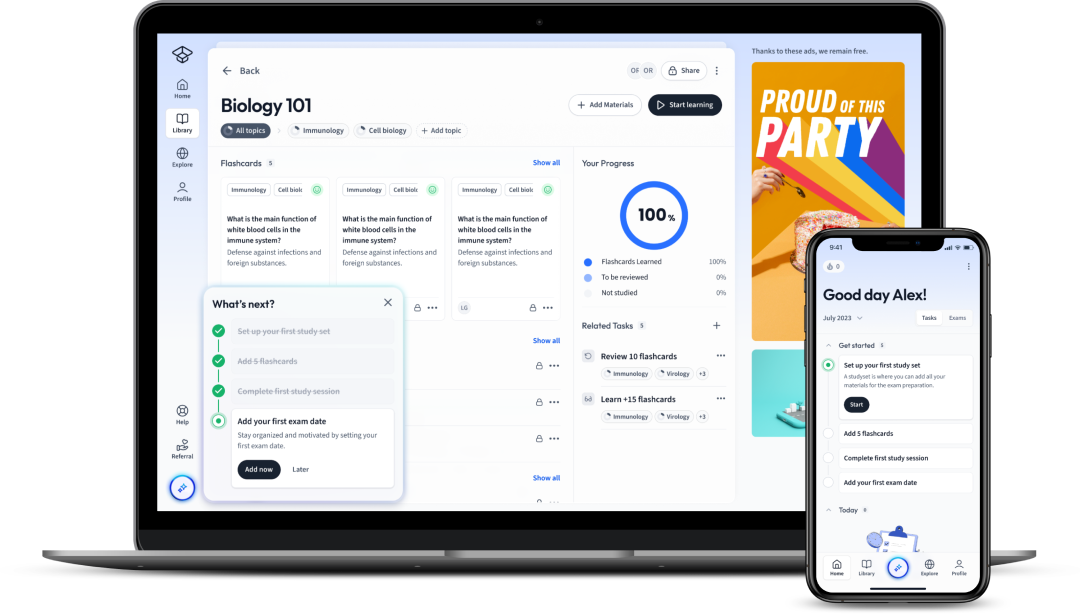
Already have an account? Log in
Open in AppHow would you like to learn this content?
How would you like to learn this content?
Free engineering cheat sheet!
Everything you need to know on . A perfect summary so you can easily remember everything.
The first learning app that truly has everything you need to ace your exams in one place
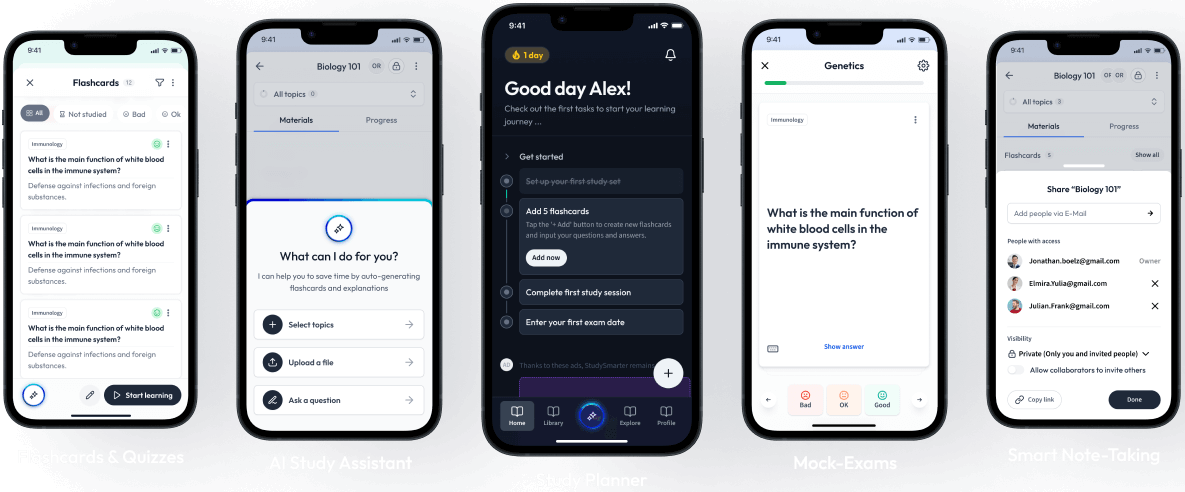
Sign up to highlight and take notes. It’s 100% free.
Save explanations to your personalised space and access them anytime, anywhere!
Sign up with Email Sign up with AppleBy signing up, you agree to the Terms and Conditions and the Privacy Policy of StudySmarter.
Already have an account? Log in