
StudySmarter: Study help & AI tools
4.5 • +22k Ratings
More than 22 Million Downloads
Free



Lerne mit deinen Freunden und bleibe auf dem richtigen Kurs mit deinen persönlichen Lernstatistiken
Jetzt kostenlos anmeldenEver seen someone wee in a pool?
We don't recommend it - besides being impolite, weeing in a pool is injurious to health. The acid in urine reacts with chlorine (used to sanitise swimming pools) and produces toxic gaseous products, which can irritate our lungs and damage our respiratory system.
So, how do you think that scientists studied this chemical reaction? They collected samples of pool water contaminated with urine to understand the risks of weeing in pools. Then, they separated and tested the samples, all so that they could identify the compounds within. Next, they studied the compounds to understand how they react and impact our health. All of this distils down to one field of chemistry: chemical analysis.
Is it possible to identify the presence of urine in a pool just by looking at it? No! Likewise, we cannot see the toxic products that urine produces on reacting with chlorine. To identify them in the pool water, we use chemical analysis.
Chemical analysis is the process of identifying, separating and quantifying the components of a sample to understand its nature and composition. The branch of chemistry that deals with chemical analysis is called analytical chemistry.
There are different types of chemical analysis, as well as various common techniques and methods. But before we jump into them, let us have a brief look at the steps of chemical analysis.
No matter the method or technique used, chemical analysis typically involves the following steps:
These steps give us a brief overview of how chemical analysis is done. Each step might have further sub-steps and include unique analytical procedures. The choice of analytical techniques or methods used depends on our sample and the type of chemical analysis we want to carry out. Let's explore the types of chemical analysis now.
Chemical analysis is classified into two major types
We'll first have a look into qualitative chemical analysis.
You taste a pizza and might feel it is too hot for your taste. What makes the pizza so spicy? Maybe it is topped with jalapeños, or perhaps pepperoni? These toppings help give the pizza its unique taste and identity.
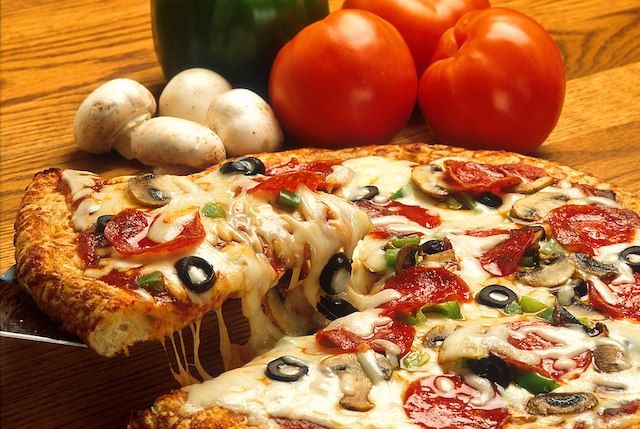 Fig. 1: Supreme pizza.
Fig. 1: Supreme pizza.
Therefore, to determine why a pizza tastes a certain way, we try to identify what it is topped with. This is a kind of qualitative analysis.
Qualitative chemical analysis is a type of analysis used to identify the substances within a sample and determine whether a particular substance is present or not.
Just like the toppings of a pizza, all the chemical samples have different constituents within them. To determine the constituents of a chemical sample, we use qualitative chemical analysis. It tells us exactly which chemical species the sample is made from, be it different molecules, elements, or compounds.
Let us consider the example of pizza again. We know that the toppings like jalapeños and pepperoni make a pizza taste hot. But how do we know how much pepperoni is added to a pizza? This question is how much of something is answered by quantitative chemical analysis.
Quantitative chemical analysis is a type of analysis used to determine the quantity or the amount of a substance in a sample.
Why might quantitative chemistry be useful? Well, what if you like a little bit of heat on your pizza, but not too much? You'd probably prefer a pizza topped with just a few slices of pepperoni. Knowing exactly how much pepperoni will be in your meal allows you to pick the perfect pizza for you.
In short, qualitative analysis deals with what is present in a sample, while quantitative analysis answers how much of the substance is there.
For your GCSE exam, you need to know about different techniques, tests, and methods used in chemical analysis. You should be able to compare them as well as discuss why you might choose one approach over another. Here is an introduction to chemical analytical techniques:
Testing for pure substances using melting and boiling points.
Testing for gases using simple test tube reactions.
Testing for ions using reactions that you can carry out in class, such as flame tests, the sodium hydroxide test, and tests for anions.
Instrumental analysis, such as chromatography and flame emission spectroscopy.
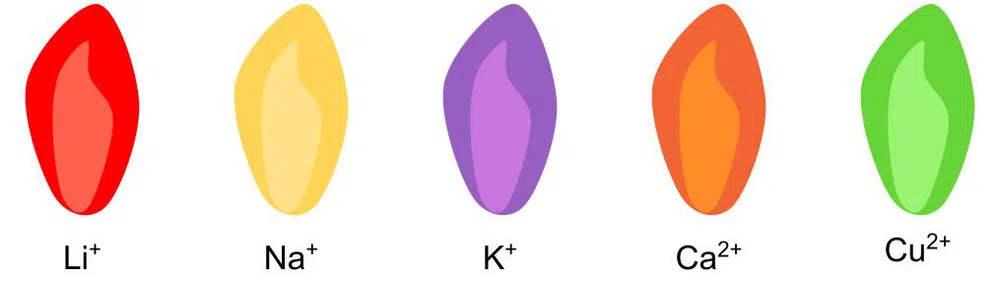 Fig. 2: A diagram showing the colours of flames produced by different ions, an example of qualitative analysis.
Fig. 2: A diagram showing the colours of flames produced by different ions, an example of qualitative analysis.
The tests for gases and the sodium hydroxide test are all simple reactions that you can try out in class. They are quick and convenient to use, but they are qualitative, not quantitative. If we want a quantitative measure of the sample, we have to use certain analytical instruments. They not only identify components of a sample, but also measure their relative amounts. Using analytical instruments in chemical analysis is called (no surprises here) instrumental analysis.
Instrumental methods have certain advantages over test tube reactions. As mentioned above, some are both qualitative and quantitative, whilst most are extremely accurate, sensitive and rapid. In addition, they can work with small samples and are highly versatile.
Here are some examples of instrumental analytical techniques:
Check out Instrumental Analysis to learn more about instrumental techniques used in chemical analysis. Additionally, you can explore some of the specific methods we mentioned above at A-level chemistry. Why not explore NMR Spectroscopy or Chromatography to find out further details about the respective subjects?
Every household product, from toiletries like shampoo and soap to food products like table salt, sugar, and sauces, is chemically analysed before it reaches you to ensure that it is non-toxic, stable, and safe to use. Given below are a few examples of the fields in which chemical analysis is used and some of its uses that you might encounter.
Field | Uses of chemical analysis | Example |
Medicine |
|
|
Food |
|
|
Environmental science |
|
|
Sports |
|
|
Chemical analysis is the process of identifying, separating and quantifying a substance in a sample.
There are two types of chemical analysis:
Qualitative chemical analysis. This identifies the presence of a substance in a sample.
Quantitative chemical analysis. This determines the amount of a substance in a sample.
Chemical analysis is the process of identifying, separating and quantifying the components of a sample to understand its nature and composition.
Chemical analysis is important to ensure, amongst other reasons:
Chemical analysis is used to:
For example, you could use chemical analysis to measure levels of air pollution, screen for allergens in toiletries, or detect toxins in food.
Chemical analysis typically follows these steps:
Qualitative chemical analysis is a type of analysis used to identify the substances within a sample and determine whether a particular substance is present or not.
Quantitative chemical analysis is a type of analysis used to determine the quantity or the amount of a substance in a sample.
Why do we test for gases?
For example:
How do you carry out the test for oxygen?
Place a glowing splint inside a test tube full of the gas.
What is the positive result of the test for oxygen?
The glowing splint relights.
How do you carry out the test for hydrogen?
Hold a lit splint over the open end of a test tube full of a gas.
How do you carry out the test for carbon dioxide?
Bubble a gas through limewater.
How do you carry out the test for chlorine gas?
Insert damp blue litmus paper into a test tube filled with gas.
Already have an account? Log in
Open in AppThe first learning app that truly has everything you need to ace your exams in one place
Sign up to highlight and take notes. It’s 100% free.
Save explanations to your personalised space and access them anytime, anywhere!
Sign up with Email Sign up with AppleBy signing up, you agree to the Terms and Conditions and the Privacy Policy of StudySmarter.
Already have an account? Log in